在多线程环境下,避免使用HashMap时存在丢失数据的情况
ConcurrentHashMap
定义
继承AbstractMap,实现ConcurrentMap
1
| public class ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements ConcurrentMap<K,V>, Serializable
|
存储结构
解决HashMap线程不安全问题有Hashtable和Collections.synchronizedMap(hashMap),
不过这两个方案基本上是对读写进行加锁操作,一个线程在读写元素,其余线程必须等待,性能较差
而ConcurrentHashMap有效解决了性能问题
在jdk1.7中,ConcurrentHashMap采用的是Segment+HashEntry的方式进行实现,如下图所示
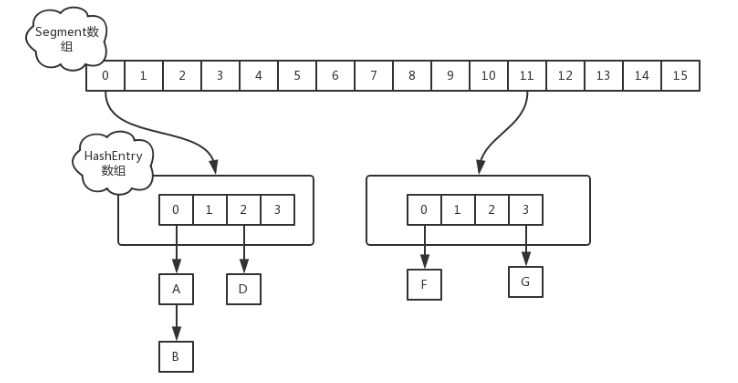
其中Segment在实现上继承了ReentrantLock,这样就自带了锁的功能,这样就相当于将整个hashmap分成
多个子map,每个segment都可以单独加锁,不属于同一个segment的结点可以并发进行操作,大大提高了性能
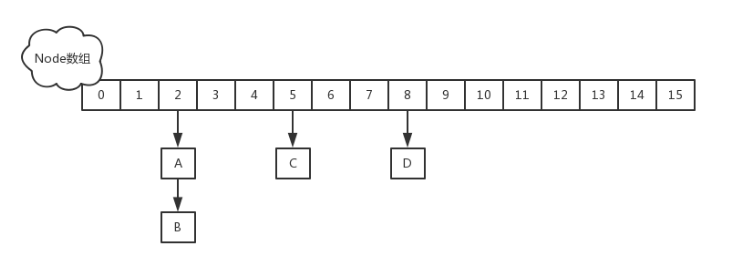
在jdk1.8中,取消了segment数组,而采用了Node数组(Table)的形式,如下图所示
Node
保存key,value及key的hash值的数据结构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
| static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; volatile V val; volatile Node<K,V> next; }
|
使用volatile关键字修饰,保证并发的可见性
put操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49
| public V put(K key, V value) { return putVal(key, value, false); } final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); int binCount = 0; for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) tab = initTable(); else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) { if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null))) break; } else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED) tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); else { V oldVal = null; synchronized (f) { if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { if (fh >= 0) { binCount = 1; for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) { K ek; } } } } } } addCount(1L, binCount); return null; }
|
找到值为key的结点e,则设置e.val = value
1 2 3 4 5 6
| if (e.hash == hash && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) { oldVal = e.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) e.val = value; break; }
|
未找到值为key的结点,则新建Node并插入链表
1 2 3 4 5
| Node<K,V> pred = e; if ((e = e.next) == null) { pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null); break; }
|
结点为红黑树结构,通过putTreeVal方法往红黑树中插入节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
| else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { Node<K,V> p; binCount = 2; if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,value)) != null) { oldVal = p.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) p.val = value; } }
|
binCount不为0,说明put操作对数据产生了影响
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
| if (binCount != 0) { if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) treeifyBin(tab, i); if (oldVal != null) return oldVal; break; }
|
initTable
table初始化操作会延缓到第一次put行为,但是put可以并发执行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
| private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() { Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc; while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) { if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0) Thread.yield(); else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) { try { if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) { int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n]; table = tab = nt; sc = n - (n >>> 2); } } finally { sizeCtl = sc; } break; } } return tab; }
|
sizeCtl默认为0,如果ConcurrentHashMap实例化时有传参数,sizeCtl会是一个2的幂次方的值
有且只有一个线程能够修改成功,其它线程通过Thread.yield()让出CPU时间片等待table初始化完成
get操作
table如果为空,返回null,否则计算key的hash值,并获取指定table中指定位置的Node节点,
通过遍历链表或则树结构找到对应的节点,返回value值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
| public V get(Object key) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek; int h = spread(key.hashCode()); if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) { if ((eh = e.hash) == h) { if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))) return e.val; } else if (eh < 0) return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null; while ((e = e.next) != null) { if (e.hash == h && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) return e.val; } } return null; }
|


